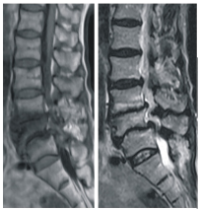
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnoses in the Lumbar Spine of Adults With Low Back Pain in South West, Nigeria
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of love back pain in Nigeria cumparable to what obtains in industrialized countries, where it is recorded a affecting inure than 80% of the populace in their liletame and accounting for a mean of 3 days off work per person per year. Although numerous modalities are available, Magnetic resonance Imaging (MRI) has emerged as the procedure af choice for the diagnosti imaging of the lumbar spine, due to its imaging characteristics which allow examiners to observe himhar anatomy in precise detail and detect morphalogic and biochemical abnormalities that were not observable previously. This study is dans sa determine the pattom, prevalence and probable cause of low back pain in adults and to compare the results with those of previous studies.
Methodology: Two hundred and fity patients who had MR imaging of lumbar spine pedarmed during a 12-month period (have 2016 May 2007 wew neviewed. An open magnet of 12TESLA strength (SIEMENS MAGNETOM CONCERTO (MR 2004A) was med to obtain images. Data woanded included dise contour, disc space narrowing/height, nerve root compression, centeal spinal stenosis, bony destruction, bone marrow changes/Modic changes, spondylosis/spondylolisthesis and the presence of paravertebral or panaspinal soft tissuemasies
Results: The mean age of the patients was 53.27±14.39 years, with majonty of the patients 23.6%) in the decade. In all 42.4% females and 57.6% were males Commonest linical finding was idiopathic hack pain in which majority (87.4%) had mechanical love back pain which comprises degenerative, idiopathic and congenital abnormalities, while 12.6% had non-michanical low back pain comprising infections and tumors. The commonest radiological diagnosis is burth genders and in all the age groups, fexwagt in the 21-30 years) мак Inter Vertebral astrochondrosis
Conclusion: Mechanical love back pain, of which intervertebral ustrochemadness accounts for th highest percentage and is the most comman cause of kne back pain in our environment
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
How to Cite
References
1. Gaskill MF, Lukan R, Wat G. Lumbar disc disease and stenosis. Radiol Clin North Am 1991, 29:735-764
2. Anderson JAD. Problems of classification of LBP Rheumatol Rehabil 1977, 16:34-36
3. Liborul-Yde C, Kyvik KO. At what age dars low back pain become a common problem? A study of 29,424 individualما aged 12-41 ywars Spine 1998, 23-228-234
4. Walker The Prevalence of Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review of the Literatune from 1966 to 1998. 1 Spinal Disord 2000 13:205-217.
5. Louw QA, Maris LD, Grimmет-батуть K. The Prevalence of low back pain in Africa a systematic revios, BMC
Musculoskelet Disord 2007, 8:15
6. Jarvik LG, Deya R.A. Diagr evaluation of love back pain with emphasis on imaging, Anne ML 282,137-586-397
7. Wandell, G., The Epidemiology of buck prain clinical standands advisory group, CHAG Report on Hack pain, HMSC), London, 1994. Pages 1-64.
8. Ackerman S1, Steinberg EP, Bryan RN, HenDebba M, Long DM. Trends in diagnostic imaging for love back pain has Ml imaging heats a substitute or add-on. Radiology 1997, 20633-538
9.Janssen ME, Bertrand SL, Joe C, Levine Ml. Lumbar bermated disk di somparison of MRI, myelography, and post-myelographic CT scan with surgical lodings Orthopedics. 1994, 17:121-127.
10,. Kent DL, Haynor DR, Larson ER, Deyo RA. Diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis in adultse a metaanalysis of the accuracy of CT, MR, and myelography AŞK Am Roentgenol. 1992, 158 1135-1144
11. Moseley IF. Salety al magnetic resonance imaging, Brit Med J 1994 30811811182.
12. Frymoyer JW, Newberg A, Tupe MH, et Spine radiographs in patients with low track pain. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1984, 66-1048-1
13. Moesland LW, Lopez-Mender A Alarcon Ge Spinal stenosis A comprehensive review of the literature Semin Asthritis Rheum. 1949, 19:327149
14. Valin E. The epidemadogy of low back pain in the nest of the world. fipow. 10, 22:1747-1754
15. Moses G, Stephen M and Didace BM. Aetiology of low back pain in Mulago Hospital. Afr Health Sci 2005, 5364-167
16. Lakadamyali H, Tarhan N., Firgun T Cakir II, Agilder A. STIK wpen for depiction of degerwatcharin posterior stallizing elements in patiesas with low back pain. ABR Am Roentgныя 2008, 1973-479
17. Deyo RA. Easty diagnostic evaluation of low back pain / Gen Intim Mal 1986, 326-338
18. Danneskiold-Samane B, Bartus M. Idiopathic low back pain. J Med. 2001, 15
19. Adams M.A. Rougfiley P. What is intervertebral disc degeneration and what was 17 При 2006, 11:2111. 2161
20. Schwanter AC, April CN, Debby H. Thi wlasive contributions of the disc and zygapophyseal joint in chronic low back pain. Spine 1994, 19. O NOK
21. Hattie MC, Videman T., l'a Lumbar disc degenenatis epidemiology and genetic interces. Spine 2004, 27 2631 3644
22. Malfair D. all DF, Imaging degenerative discurs of the lumbar spins. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2007, 1 221-238
23. M, MA V. L. The Imaging of Spinal Pathology, Goinger R G. Allison D. J. Diagnosts Radiology, vulume 1, thint edition, Sheffald and Landon 1997-2167 2173.
24. Enemann DR, O'Danahue, Rulin Rot al CSF pubsations within non-croplastic spinal cand cysts. AINE Am Neuroradiol 19871752
25. Alyas Baifuddin A, Comel D. MR Imaging evaluation of the bone marrow and manow imfiltrative disorders of the lumbar spine. Magn Reson Imaging N Am 2007, 15 190 219
26. Algra Pit, Worm 11, Timing H, et al. Detection of vertebral metastas comparison between MR imaging and hone tugraphy Radiographus 191 11:210-212
27. Tall MA, TAK, Very T Palka P. MR Imaging of the spinal bone marrow. Magn Ranon Imaging Clin N Am 2008, 15 175 196
28. Ples DM. Estramedullary spinal humors. Haags R, Lantieri CJ, Gilken RC-CT anst MK Imaging of the the whole s body, Volume 1, fourth edition, Mosby, Missouri, 2003, Page 710-782.
29. Valal LA, Murphey M.D. Primary tumurs of the wя пране. Мади Кап Imaging Clin N Am. 2007 1 299 203
30. Vaughan 11, Winder, IR, Lanstein 1. Johnson R., Dunnington). L. Non Hodgkin Lymphoma of the Spine. A Report of Three Cases with a Minimor Ten-Yiar Fllow-up.hew Joint Surg Am 1998, 183104-110
31. VAD., Muulopndos LA Comuliamos A, vt al. The Wrap-around MR siga telltale sign of lymphoma ul the hone marrow. Eur Radiol 177
32. Larvulon A. A, Munck N, Sap 1.G. Can clinical data help to serve patarnis with lymphama for MR imaging of bone marrow? Ano Oniul 1995,6-795-HO
33. Van FC, Rhodes JR., Stump AF Speal infections late//emediciw.medscape.com/article 26 Accom 26287